Noneconomic elements (one dimension) and intrinsic and extrinsic elements (second dimension) Intrinsic elements come from the product itself (they are the economic and non value concerns what customer wants to have happen Finally value judgement concerns an assessment of the value, it is the assessment of what has happened Wilson and And the wants that can be satisfied with goods and services of any kind are economic wants Like for example food, shelter, clothing, etc are economic human wants And those which cannot be bought are noneconomic wants like peace, love, affection, etc All human wants to have some basic common characteristicsA few things that we want, are not purchased from the market by paying a price Such wants are called noneconomic wants For example, we want air to breathe, rain water for agriculture etc When we want a maid to cook, it is our economic want But if the food is cooked by mother, it becomes noneconomic want INTEXT QUESTIONS 22 1
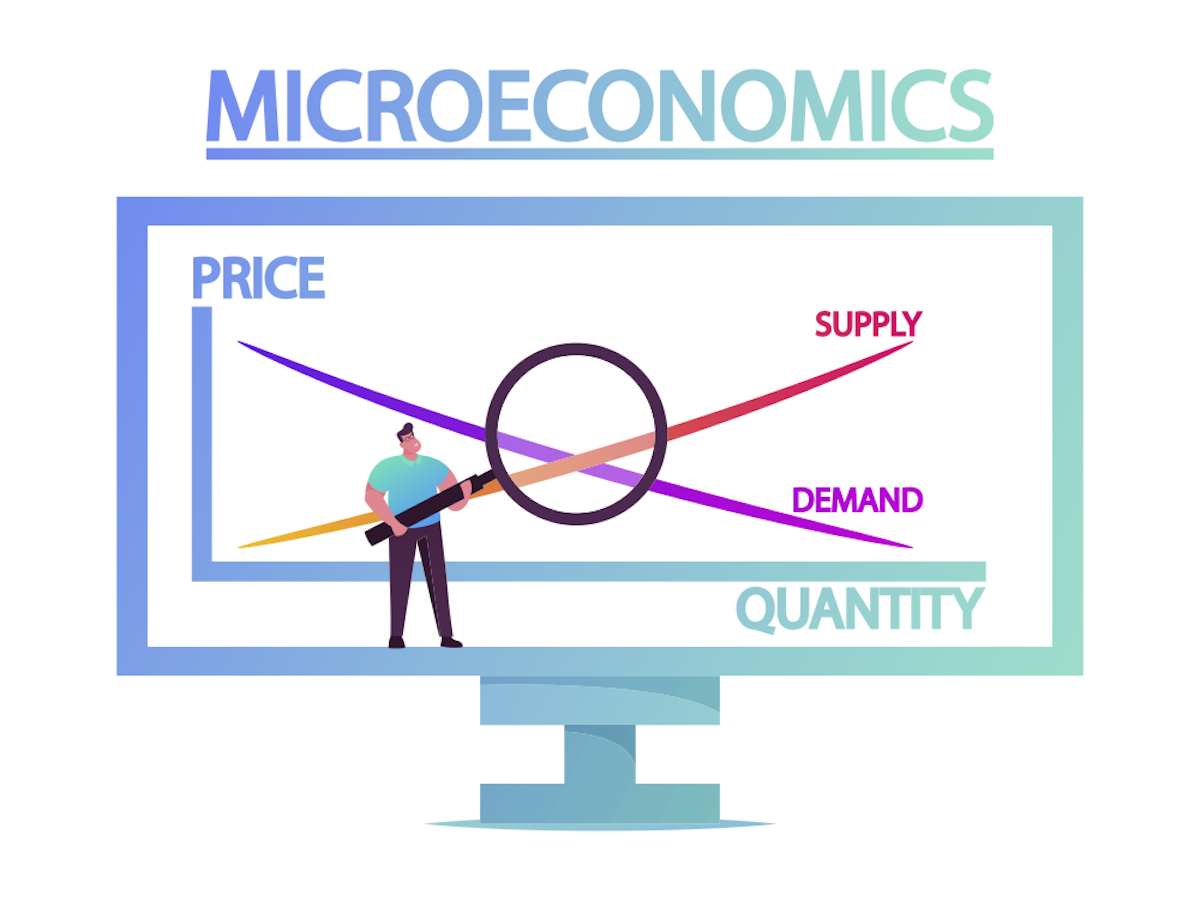
Microeconomics Explains Why People Can Never Have Enough Of What They Want And How That Influences Policies
Non economic wants definition
Non economic wants definition- Noneconomic definition is not economic;Economic Goods and Free Goods Most goods (and services) are economic goods, ie they are scarce Scarce goods are those for which the demand would be greater than the supply if their price were zero Because of this shortage, economic goods have a positive price in the market That is, consumers have to pay to get them




Explain The Difference Between Economic Andnon Economice Activities Brainly In
What is a noneconomic loss benefit? Answer The main difference between economic and noneconomic activities lies in the fact that the economic activities are carried out to satisfy human needs, whereas noneconomic activities are performed for gaining psychological satisfaction So, check out this article to get some more differences amidst these two types of human activitiesView Test Prep Objective 501 Study Guide (1) from MATH 108 at University of the Fraser Valley Objective501StudyGuide 1 Which of the following items would be considered a noneconomic want
Needs and Wants Defined Needs are based on physiological, personal, or socioeconomic requirements necessary for you to function and live Transportation is a need for the modern, urban person Conclusion With the above discussion, it is quite clear that the only aspect which distinguishes these two activities is the objective The same activity can be economic and noneconomic at the same time, you can understand this with an example, Suppose a father is taking his child to school by Van, this is a noneconomic activity, as he drops his son out of affection andEconomic Wants The desire for scarce material and services NonEconomic Wants Desires for nonmaterial things that are not scarce, such as air, sunshine, frienship, and happiness Utility The ability of a good or a service to satisy a want Producer Anyone that creates a utility
Especially having no economic importance or implicationDAAAM INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC BOOK 14 pp Chapter 11 IMPORTANCE OF NONECONOMIC FACTORS FOR ECONOMICS LETUNIC, S & DRAGICEVIC, M Abstract Important economists who have pointed out existence of economic and non economic factors are already AMarshall than GMyrdall and ASen The analysis of the social situation and system is grateful (such analysis is mainly used in economicNoneconomic damages look more to compensating for the intangible loss of plaintiff's injury Pain and suffering is the most common type of noneconomic damages, though others include disfigurement, permanent impairment, and loss of enjoyment of life These damages are not as clear and easy to identify and place a dollar amount on for



Human Wants How Resources Satisfy Wants Economic And Non Economic Wants Flexiprep




What Non Tax Filers Need To Know About Economic Impact Payments Consumer Financial Protection Bureau
Macroeconomics is the part of economic theory that studies the economy as a whole, such as national income, aggregate employment, general price level, aggregate consumption, aggregate investment, etc Question 5 Distinguish between a centrally planned economy and a market economy Answer Out of syllabusIf you have a permanent impairment due to a workrelated injury or illness, you are eligible for a noneconomic loss benefit under Section 46 of the Workplace Safety and Insurance Act, 1997 (WSIA) We pay you a noneconomic loss benefit when you have an ongoing impairment after your workrelated injury or illness has reached a point where it is notIn 16, 277 million people usually worked part time (that is, they usually worked less than 35 hours a week) 1 Parttime workers are categorized by the reason they work part time—economic or noneconomic 2 Most analysis of parttime work concentrates on people working part time for economic reasons—often called "involuntary parttime workers"—because of the cyclical nature




1 Objectives 1 Describe Economic Concepts That Apply To Satisfying Economic Wants 2 Explain The Role Of Capital Formation In An Economy Warm Up Explain Ppt Download




Turkey S Economy Remains Vulnerable American Enterprise Institute Aei
The same activity may be economic as well as noneconomic For example, a nurse attending a patient in a hospital is an economic activity as the nurse works for a salary But when the same nurse attends to her sick mother at home it is a noneconomic activity because the object isAn economic good is just something that is of limited availability, relative to how much people want it It is something that is defined by scarcity Most things fit the idea of an economic good Cars, food, watches, pants, and peanuts, for example While "economic goods" are characterized by scarcity, "noneconomic" goods do not sufferChapter 02 The Economizing Problem Printer Friendly The foundation of economics is the economizing problem society's material wants are unlimited while resources are limited or scarce Unlimited wants (the first fundamental fact) Economic wants are desires of people to use goods and services that provide utility, which means satisfaction




Entrepreneurs Satisfy Needs And Wants




5 30 Analyzing Sales Process
The economic environment of business of modern times is highly complex Total economic environment is consisting of prevailing economic system, basic economic philosophy and economic policies of the government, stages of economic development, agricultural and industrial production, infrastructure, planning process, trade cycles, national income, savings, population,Its economic function can be contrasted with barter (nonmonetary exchange) Given a diverse array of produced goods and specialized producers, barter may entail a hardtolocate double coincidence of wants as to what is exchanged, say apples and a bookClassification of Wants Wants can be classified in following ways (i) Economic and NonEconomic Wants The wants which cannot be satisfied by such goods and services that can be bought are known as economic wants For example, want for food, want for book, want for dress etc To satisfy these wants, a consumer has to spend money



Economicsdiet Com




Noneconomic definition at Dictionarycom, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation Look it up now! Scarcity refers to the most basic economic problem the gap between limited—that is, scarce—resources and theoretically limitless wants Example of Wants While food is the basic need and without food, one cannot survive but eating that food in silver or gold plates daily is an example of want which only a few rich people can fulfill While the shelter is the basic need but residing in 5 bedroom apartment in the posh locality or constructing a 00 yards farmhouse for himself or




Economics Economics Defined Economy The Organized Way A



Jojocomputer In
To ensure business continuity and further economic recovery, the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) yesterday proposed the opening of all businesses at varied operating capacities under Alert Levels 1 to 4, except for those considered high risk and nonessential "We propose hopefully that we allow the MSMEs (micro, small and medium enterprises), businesses to According to the World Bank, the US now has by far the highest tariff rates in the entire developed world (excluding a couple of tiny places like Bermuda) I used to hear people say that the US was a free trading nation and that our trade partners had lots of barriers That was not true, as in recent decades the US tariff rates (and nontariff barriers) were similar to otherExtract of sample "Economic versus NonEconomic Issues in Union Environments (Employee Labor and Relations class) Human Resource Management" INTRODUCTION & OVERVIEW The following is an analysis of a noneconomic, and then an economic article from a contract agreement between the AmericanGuild of Musical Artists and the Producing Office and




11th State Board Economics Classification Of Wants Lecture 9 sawa Brothers Youtube




Needs And Wants Economic View
Such activities are known as human activities These activities are broadly classified as economic and noneconomic activities While economic activities are those c By Col Mukteshwar Prasad(Retd) Needs and Wants (Economic View) 2 Difference Between Needs and Wants We all know that economics is a social science, which deals with production, distribution and consumption functions It is all about making choices regarding the allocation of scarce resources, so as to make their best possible use and satisfyExample #1 – Supply and demand This example of Economics is the most basic concept of freemarket economics that helps in determining the right price for a good or service Eg a startup company wants to introduce a fresh product into the market and wants to find the right price for its product Let's say the product costs $100 to the




Essential Standard 5 00 Understand Economics Ppt Download




Main Types Of Non Economic Activities Performed By Children By Sex Download Scientific Diagram
Every human being keeps himself occupied in some activity to satisfy human wants;NonEconomic Activity A noneconomic activity is an activity performed with the purpose of rendering services to others without any considerations of financial gains Activities that are initiated for personal content or for meeting human sentiments are noneconomic activities Some common examples of noneconomic activities are the following Noneconomic goods are goods or services that are plentiful and free Air and dirt are considered noneconomic goods since they are neither scarce nor valuable There is much debate over the value of goods such as food, shelter and health care While these are economic goods, many argue that necessities for basic survival should be free
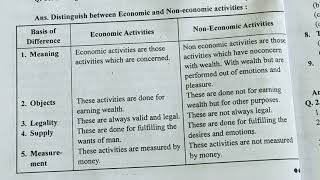



Difference Between Economic And Non Economic Activities Explanation In Hindi Youtube




Non Economic Wants Example
Define noneconomic noneconomic synonyms, noneconomic pronunciation, noneconomic translation, English dictionary definition of noneconomic adj not of or relating to economic factors noneconomic benefits




1 Chapter 3 Economic Environment Of Business 2 Lesson 3 1 Economic Wants Goals Describe Economic Concepts That Apply To Satisfying Economic Wants Explain Ppt Download




Explain The Difference Between Economic Andnon Economice Activities Brainly In
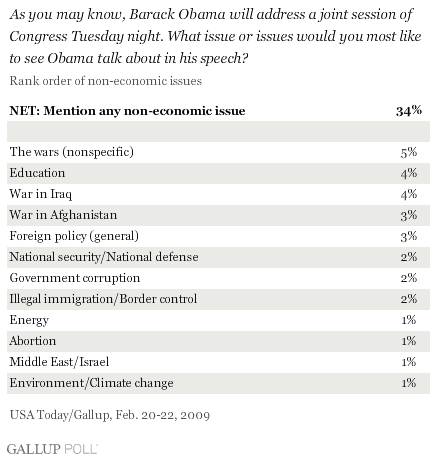



Americans Tell Obama What They Want To Hear In Speech




The Difference Between Wants Vs Needs In Economics Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



1




Statistics For Economics On Vimeo




Lesson 2 1 Entrepreneurs Satisfy Needs And Wants




Ppt Entrepreneurs In A Market Economy Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Lesson 1 Fundamentals




How Do Non Economic And Economic Wants Differ Quora



Difference Between Economic And Non Economic Activities With Comparison Chart Key Difference




Microeconomics Explains Why People Can Never Have Enough Of What They Want And How That Influences Policies




Opinion Economic Incentives Don T Always Do What We Want Them To The New York Times




What Are The 4 Types Of Economic Goods Boycewire
/law_of_demand_chart2-5a33e7fc7c394604977f540064b8e404.png)



Law Of Demand Definition Basic Economics




Introduction To Business 11




What Is Economic Activity Definition And Examples




5 Macroeconomic Goals Intelligent Economist



The 5es Of Economics



Apopenschool Ap Gov In



Hetecon Net




Ppt Chapter 3 Economic Environment Of Business Powerpoint Presentation Id




Essential Standard 5 00 Understand Economics Ppt Video Online Download




Theory Of Consumer Behavior Pdf Economic Surplus Utility



Difference Between Economic And Non Economic Activities With Comparison Chart Key Difference




Economic Versus Non Economic Wants Economist Point Youtube




Economic Wants Vs Non Economic Wants Economics Portal Youtube
/EconomicCapitalEC2-18dde4324e024d53af3b7f46fe79a1dc.png)



Economic Capital Ec Definition




1 Nature And Scope Of Economics Sauda Solved Scanner 1 1 Nature And Scope Of Economics




Doc Micro Clyde Pena Academia Edu




Basic Concepts Of Economics a Llb 301 Kslu Studocu




Economics Screen 2 On Flowvella Presentation Software For Mac Ipad And Iphone
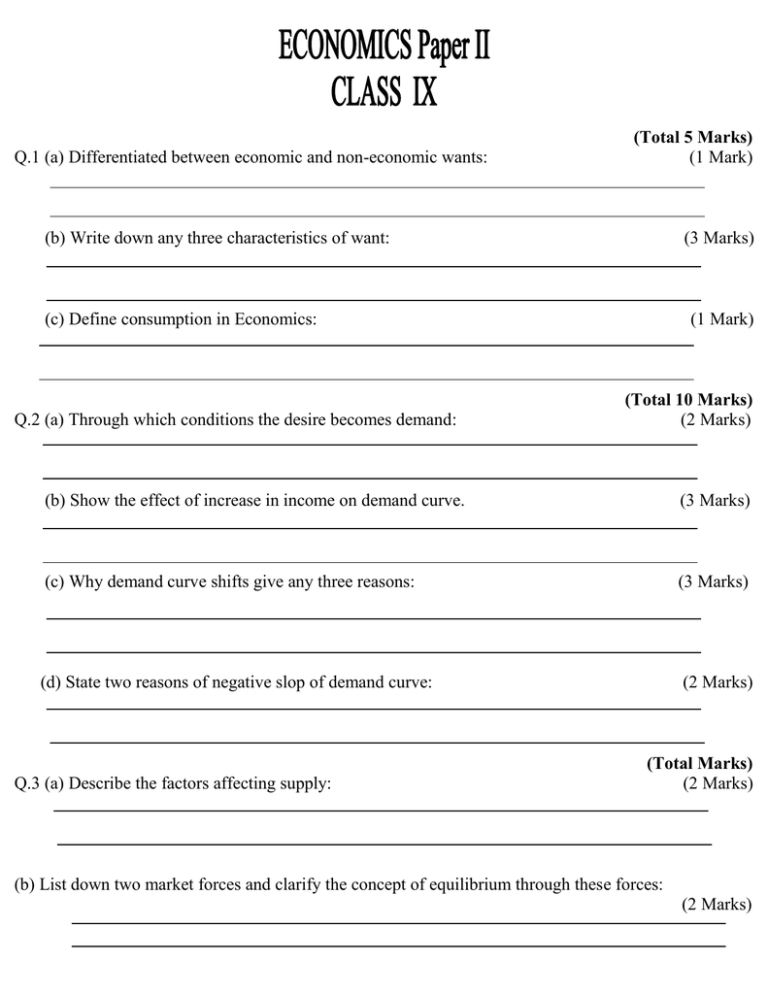



Q 1 A Differentiated Between Economic And Non Economic Wants Total 5 Marks




What Is The Difference Between Economic And Non Economic Activity Quora




Economic Goods And Services What I Want You



Economic Wants




What Is The Difference Between Economic Wants And Non Economic Wants Brainly In



Economics Screen 2 On Flowvella Presentation Software For Mac Ipad And Iphone
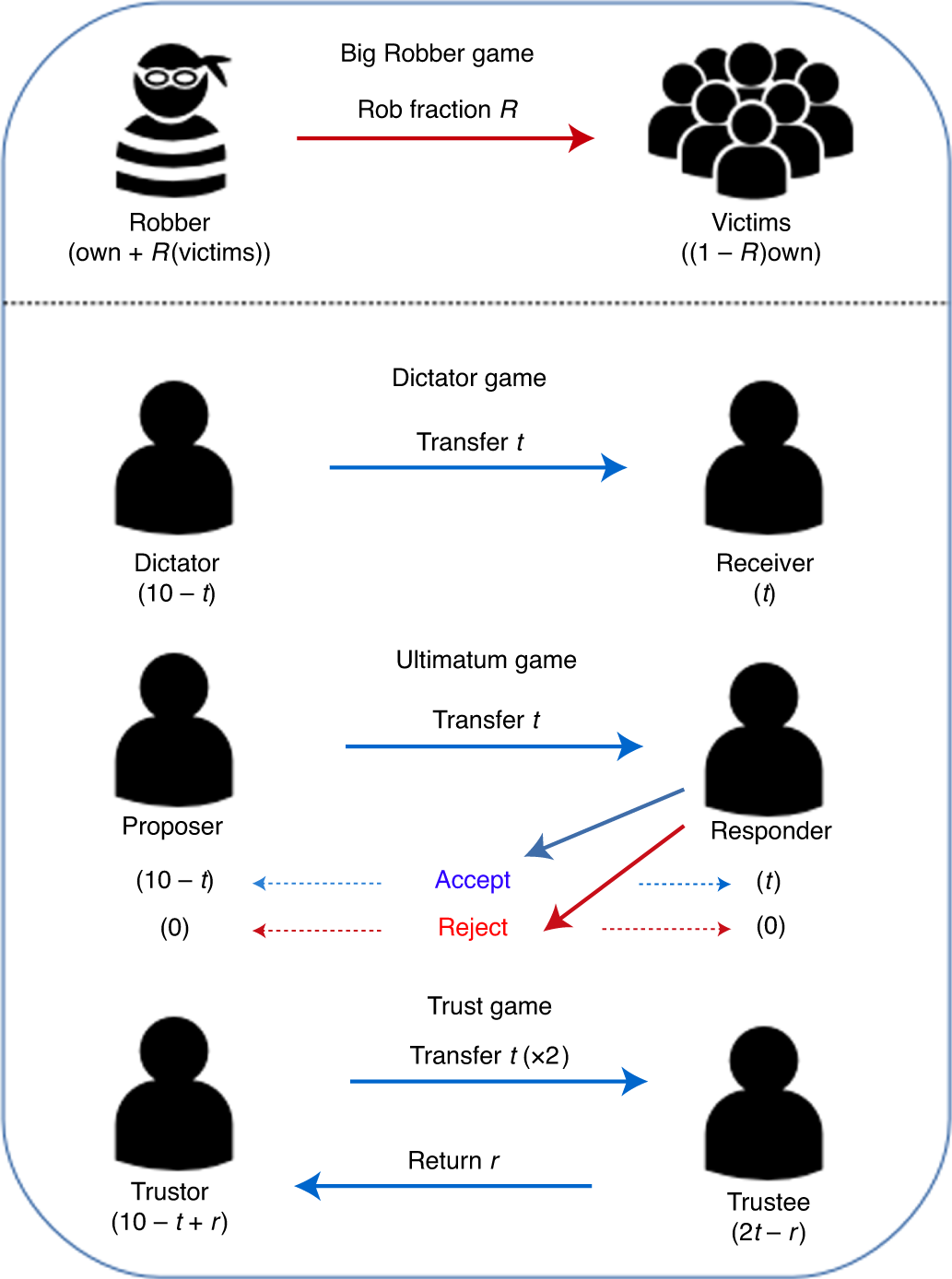



Generous With Individuals And Selfish To The Masses Nature Human Behaviour




Economic Wants By Doria S Dandies Teachers Pay Teachers




Economic Needs And Wants Definition Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Economic Versus Non Economic Wants Economist Point Youtube



3



Mba Research Lap Ec 902 Get The Goods On Goods And Services Economic Goods And Services Download Lap Ec 902



Economic Human Wants Meaning Nature Classification With Examples
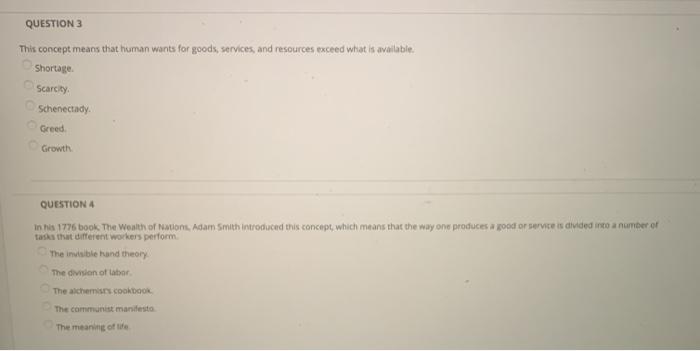



Solved Question 1 Economics Is Greatly Impacted By How Well Chegg Com



Differentiate Between Economic And Non Economic Activities Economics Topperlearning Com M5mu3kd77



2




Economic Wants And The Filipino Citizen By Hazel Bliss




Chapter 8 Project Screen 3 On Flowvella Presentation Software For Mac Ipad And Iphone




Distance Between Economic And Non Economic Activities Brainly In




Economics Unit Ppt Download




Chapter 3 1 Economic Environment Of Business Chapter




How Do You Think Non Economic People Wants Help In Promoting Social Welfare Brainly Com




What Are Unlimited Wants Definition And Examples Market Business News




1 Chapter 3 Economic Environment Of Business 2 Lesson 3 1 Economic Wants Goals Describe Economic Concepts That Apply To Satisfying Economic Wants Explain Ppt Download



Economic



What Is The Economy All About القصة المصورة من قبل 7092c236




Entrepreneurs In A Market Economy Ppt Download



2




41 Needs And Wants Ideas Teaching Social Studies Social Studies Activities Kindergarten Social Studies




Ppt What Is The American Dream Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




What Are The 4 Types Of Economic Goods Boycewire




Black Power Blueprint President Ona Zene Yeshitela Wants Wants To Personally Thank Clifbar For Donating To Apedf And Recognizing That Systemic Change Is Rooted In African Economic Self Reliance And Self Determination
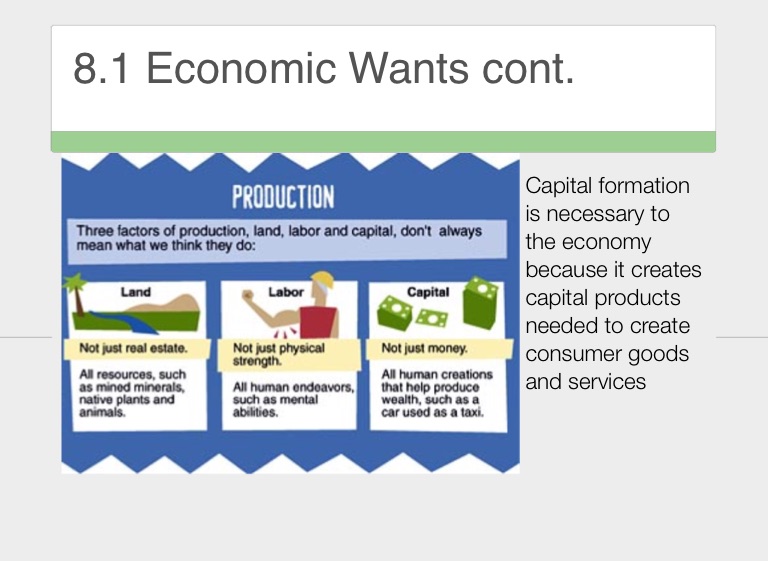



Chapter 8 Screen 3 On Flowvella Presentation Software For Mac Ipad And Iphone




Could Amsterdam S New Economic Theory Replace Capitalism Time




Needs And Wants Economic View
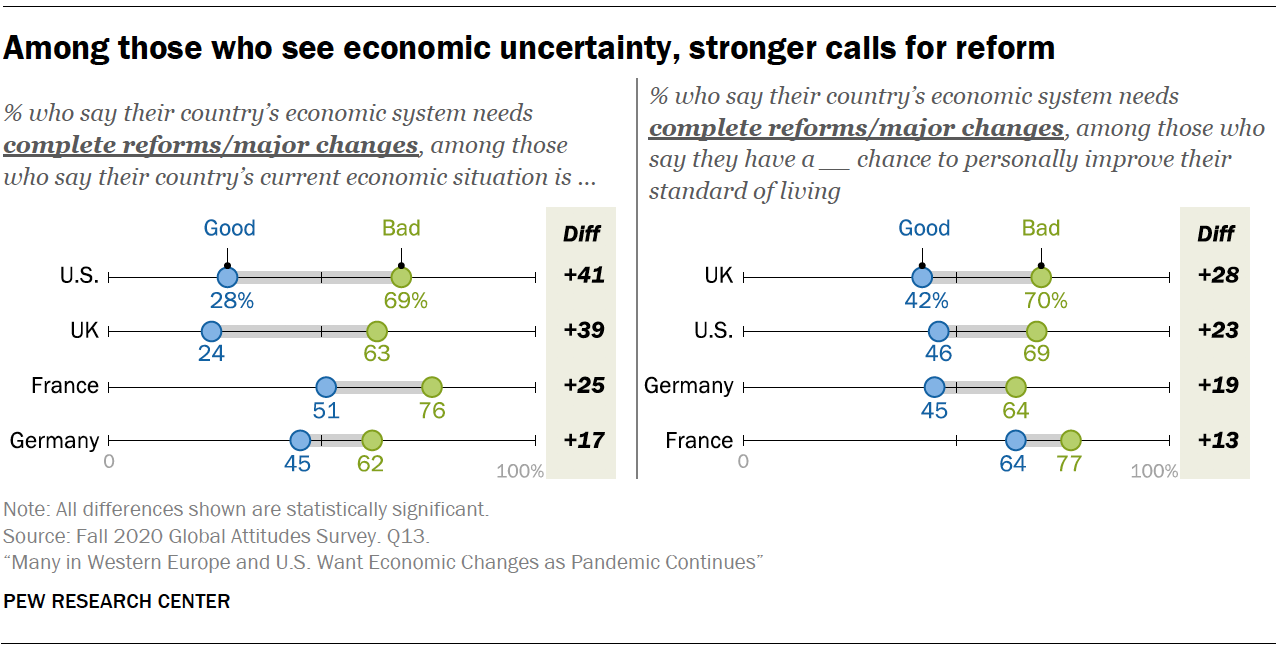



Many In Western Europe And U S Want Economic Changes As Pandemic Continues Pew Research Center




Ch 1 Section Check Questions Econ 2105 Macro Economics Docsity



2



Difference Between Needs And Wants With Comparison Chart Key Differences



Steve Sack S Cartoon For 7 6 09



The 5es Of Economics



The 5es Of Economics




The Creator Economy Needs A Middle Class




Ch 2 Economic Environment Of Business Ppt Download




E Worker For Econo Marla Is An Associate At Chegg Com



Economics Human Wants Satisfaction Characteristics And Types Of Wants Flexiprep




Explain The Concept Of Economics And Economic Activities Ppt Download




1 Concept Nature Of Business Goods Profit Accounting



Non Economic Reasons The Fed Is Tapering




Mamush Melese Dibila Posts Facebook



Statistics For Economics On Vimeo




1 Objectives 1 Describe Economic Concepts That Apply To Satisfying Economic Wants 2 Explain The Role Of Capital Formation In An Economy Warm Up Explain Ppt Download



Economics Human Wants Satisfaction Characteristics And Types Of Wants Flexiprep




Entrepreneurs Satisfy Needs And Wants




Amazon Com Covid 19 The Great Reset Schwab Klaus Malleret Thierry Books



2



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿